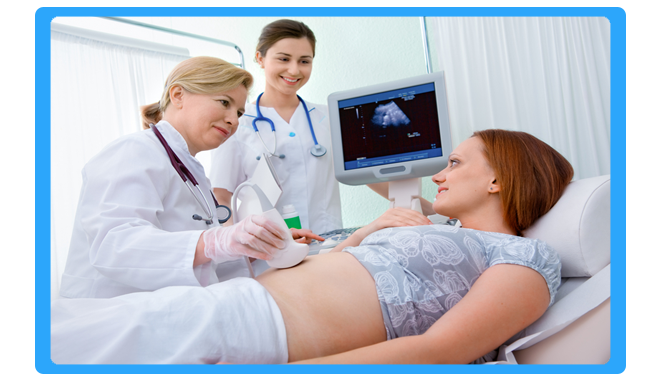
Ultra Sonography Services
The basic principle of ultrasonography is the same as that of depth-sounding in oceanographic studies of the ocean floor. The ultrasonic waves are confined to a narrow beam that may be transmitted through or refracted, absorbed, or reflected by the medium toward which they are directed, depending on the nature of the surface they strike.
In diagnostic ultrasonography the ultrasonic waves are produced by electrically stimulating a crystal called a transducer. As the beam strikes an interface or boundary between tissues of varying density (e.g., muscle and blood) some of the sound waves are reflected back to the transducer as echoes. The echoes are then converted into electrical impulses that are displayed on an oscilloscope, presenting a “picture” of the tissues under examination.
Ultrasonography can be utilized in examination of the heart (echocardiography), in location of aneurysms of the aorta and other abnormalities of the major blood vessels, and in identifying size and structural changes in organs in the abdominopelvic cavity. It is, therefore, of value in identifying and distinguishing cancers and benign cysts. The technique also may be used to evaluate tumors and foreign bodies of the eye, and to demonstrate retinal detachment. Ultrasonography is not, however, of much value in examination of the lungs because ultrasound waves do not pass through structures that contain air.
A particularly important use of ultra-sonically is in the field of obstetrics and gynaecology, where ionising radiation is to be avoided whenever possible. The technique can evaluate fatal size and maturity and placental position. It is a fast, relatively safe, and reliable technique for diagnosing multiple pregnancies. Uterine tumours and other pelvic masses, including abscesses, can be identified by ultra-sonography.
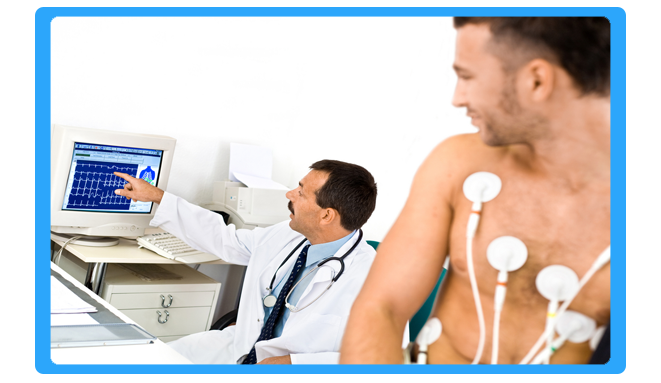
Cardiology Services
Cardiology is a branch of medicine dealing with disorders of the heart be it human or animal. The field includes medical diagnosis and treatment of congenital heart defects, coronary artery disease, heart failure, valvular heart disease and electrophysiology. Physicians who specialize in this field of medicine are called cardiologists, a specialty of internal medicine. Pediatric cardiologists are pediatricians who specialize in cardiology. Physicians who specialize in cardiac surgery are called cardiothoracic surgeons or cardiac surgeons, a specialty of general surgery.
Cardiology is a specialty of internal medicine. To be a cardiologist in the United States, a three-year residency in internal medicine is followed by a three-year fellowship in cardiology. It is possible to specialize further in a sub-specialty. Recognized sub-specialties in the United States by the ACGME are:
- Cardiac electrophysiology: Study of the electrical properties and conduction diseases of the heart.
- Echocardiography: The use of ultrasound to study the mechanical function/physics of the heart.
- Interventional cardiology: The use of catheters for the treatment of structural and ischemic diseases of the heart.
- Nuclear cardiology: The use of nuclear medicine to visualize the uptake of an isotope by the heart using radioactive sources.
- Recognised sub-specialities in the United States by the American Osteopathic Association Bureau of Osteopathic Specialists (AOABOS) include:
- Clinical cardiac electrophysiology
- Interventional cardiology
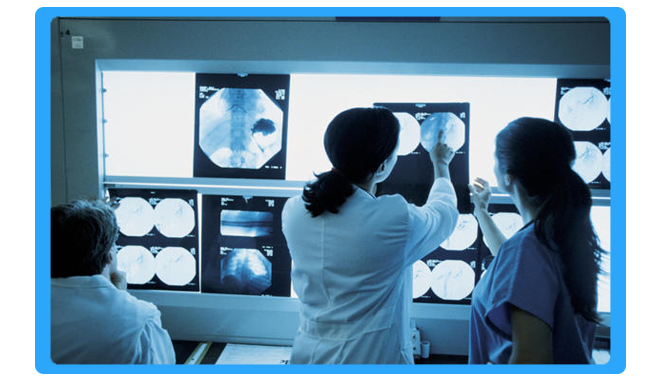
Radiology Services
Radiology is a medical specialty that uses imaging to diagnose and treat diseases seen within the body. Radiologists use a variety of imaging techniques such as X-ray radiography, ultrasound, computed tomography (CT), nuclear medicine including positron emission tomography (PET), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to diagnose and/or treat diseases. Interventional radiology is the performance of (usually minimally invasive) medical procedures with the guidance of imaging technologies.
-
- Digital radiography is a form of X-ray imaging, where digital X-ray sensors are used instead of traditional photographic film. Advantages include time efficiency through bypassing chemical processing and the ability to digitally transfer and enhance images.
- Barium X-ray is a radiographic (X-ray) examination of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Barium X-rays (also called upper and lower GI series) are used to diagnose abnormalities of the GI tract, such as tumors, ulcers and other inflammatory conditions, polyps, hernias, and strictures.
- Urology X-ray beams are passed through the abdomen, producing images of the kidneys, ureters, and bladder on a special type of film. KUB radiography is often used as a first step in diagnosing problems of the urinary system, and is usually done in conjunction with intravenous pyelography.

Pathology Services
Pathology is a significant component of the causal study of disease and a major field in modern medicine and diagnosis. The term pathology itself may be used broadly to refer to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of bioscience research fields and medical practices (including plant pathology and veterinary pathology), or more narrowly to describe work within the contemporary medical field of “general pathology,” which includes a number of distinct but inter-related medical specialties which diagnose disease mostly through the analysis of tissue, cell, and body fluid samples.
As a field of general inquiry and research, pathology addresses four components of disease: cause/etiology, mechanisms of development (pathogenesis), structural alterations of cells (morphologic changes), and the consequences of changes (clinical manifestations). In common medical practice, general pathology is mostly concerned with analysing known clinical abnormalities that are markers or precursors for both infectious and non-infectious disease and is conducted by experts in one of two major specialities, anatomical pathology and clinical pathology. Further divisions in speciality exist on the basis of the involved sample types (comparing, for example, cytopathology, hematopathology, and histopathology), organs (as in renal pathology), and physiological systems (oral pathology), as well as on the basis of the focus of the examination (as with forensic pathology).
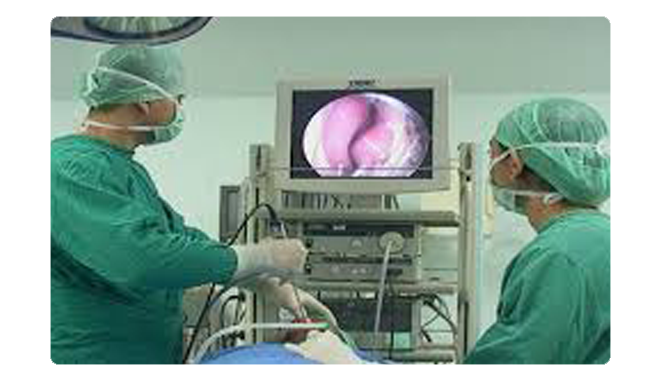
Pharyngoscopy Surgery
-
A pharyngoscopy is often used to examine the back of the throat. The two types of pharyngoscopy are indirect pharyngoscopy and direct pharyngoscopy.
During an indirect pharyngoscopy your doctor places small mirrors at the back of your mouth to clearly examine your throat, the base of your tongue and part of your larynx. -
A direct pharyngoscopy involves a fiber optic source that uses a flexible, lighted, narrow tube which may be inserted into the mouth or nose so that your doctor can examine hard-to-see areas such as the larynx and behind the nose.